YOUR GO-TO GUIDE TO PLANT-BASED PROTEIN
WARNING: THIS PAGE CONTAINS POWERFUL INFORMATION AND IS PACKED FULL OF PROTEIN CONTENT
PROTEIN DEFINED: Like Your Muscles
We know we need it but what exactly is protein?
Protein is a macronutrient that is needed to perform various functions throughout the body. It deserves an award for best leading and supporting actor for all the parts it plays in keeping us alive.
Proteins are made up of long chains of amino acids. Some of which the body produces on its own and some we must get from food.
There are 20 amino acids that when combined into various different sequences, regulate processes that go on inside every cell of the body.
ESSENTIAL & NON-ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS
(Unlike workers in a pandemic, we need them all)
There are 20 essential amino acids; eleven of these amino acids are produced by the body. These are the non-essential amino acids.
It is not essential that we consume these amino acids in the foods we eat.
Non-essential Amino Acids
Essential amino acids are the 9 amino acids that need to be consumed by eating foods that contain them.
Essential Amino Acids
COMPLETE & INCOMPLETE PLANT-PROTEINS
Can I get all the essential amino acids from plants?
Yes, absolutely! Some plant proteins contain all of them and some just a few.
Complete proteins are a singular food source that contain all 9 essential amino acids.
Incomplete proteins contain some but not all of the essential amino acids.
It’s not necessary to eat complete proteins at every meal. Aim to eat a variety of plant-based proteins throughout the day and week. Remember, variety is the spice of life!
COMPLETE PLANT PROTEINS
Amaranth
Buckwheat
Chia Sees
Hemp Seeds
Quinoa
Soy
Spirulina
Tempeh

Reasearchers now understand that your body can pull amino acids from its reserves to make incomplete protein complete. It’s the total amount of protein you eat over the day, not the specific type of protein, that matters.
-Runners World
PROTEIN, WHAT HAVE YOU DONE FOR ME LATELY?
What is the role of protein in the body?
Protein has its little amino acid hands in just about everything and every cell. Here are some highlights of how a serving of protein serves you.
TRANSPORTERS
Proteins carry oxygen, glucose, vitamins and fats through the bloodstream and throughout the body.
REGULATORS
Proteins play a role in regulating bodily fluids and maintaining pH balance in the body.
CREATORS
Proteins create antibodies for fighting off sickness, they repair cells and create new cells.
PROTEIN & PHYSICAL HEALTH
Mirror, mirror on the wall can protein make me lean and small or grand and swole?
PROTEIN FOR MUSCLE GAINS
Are you
BICEP-TUAL?
PROTEIN FOR WEIGHT LOSS
My
HOURGLASS SHAPE
is always half full
If you train on the regular, are an endurance athlete or have a physically demanding job, you should be consuming a higher percentage of protein as a part of your daily caloric intake.
Eating a higher percentage of protein versus carbs and fats can also aid in weight loss and help in keeping the weight off. Plus, increased protein intake will help maintain your muscle mass as you drop the pounds.
How does protein affect muscle mass?
Significantly upping your protein intake while also incrementally increasing the intensity of a consistent strength training routine will increase muscle mass and strength over a prolonged period of time.
Protein is also important for muscle recovery and repair, especially after strenuous training.
How does protein affect weight loss?
Protein satiates your hunger faster and helps you stay full longer when compared to both carbs and fats.
The Science: studies show that protein affects the level of the hormone gherlin in the body and acts to decrease it. Gherlin is a hormone that signals hunger.
So it goes a little something like this. Eat protein, decrease gherlin, feel full, stay full and avoid those extra calories from snacking.

WE INTERRUPT YOUR PROGRAM FOR A NOT-SO-SURPRISING FUN FACT
The current Western diet gets the majority of energy-derived calories from carbohydrates.
Our hunter-gather ancestors got the majority of energy-derived calories from protein. Makes sense as to what was available at the time and also worked to their advantage since it wasn’t always known when the next meal was coming.
CURRENT WESTERN DIET
PROTEIN: 16%
CARBS: 49%
FAT: 35%
ANCESTRAL DIET
PROTEIN: 19-35%
CARBS: 22-40%
FAT: 28-47%
AND NOW BACK TO YOUR REGULARLY SCHEDULED PROTEIN, I MEAN PROGRAM
As with most things in life, balance is key. This is especially true with weight loss goals. Don’t go protein crazy and consume all protein on site. Excess protein is typically stored as fat so it is important to consider the whole diet.
Keep tabs on daily caloric intake. To lose weight, you need to consume fewer calories than you burn. If you maintain your daily calories in and calories burned goal AND increase the amount of protein you consume then you are well on your way to losing weight and keeping it off.
Need help figuring out where to start?
Check out the calculators below to set a baseline for your calorie and protein needs.
PROTEIN PRO TIPS
Eat a protein rich breakfast to help curb hunger and cravings throughout the day.
To lose weight and keep it off, aim for 30% of your daily caloric intake to come from proteins.
Eat the protein portion of your meal first to satiate hunger and feel full faster.
PROTEIN FOR EVERY BODY
How much you need, bruh?
How do physical and biological factors affect protein needs?
Whether you’re looking to make gains, lose weight or if you just want to make sure you’re consuming an adequate amount of protein for your age, body type and activity level, it is important to know your protein needs. The information detailed below, along with the online calculators, will help you figure out how much protein you need daily.
-
The lowest amount of protein required daily to prevent deficiency is .36 grams per pound of body weight ( .8 grams per kg)
-American Dietetic Association (ADA): recommends a minimum of 52-94 grams/day
-The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC): recommends 49-171 grams/day (10-35% of daily caloric intake)
-World Health Organization (WHO): states the safe lower limit of 43 grams/day
-
Active adults and individuals looking to lose weight should get between .54 - .77 grams of protein per pound of body weight.
Athletes and adults that train intensively (6-7 days a week) should aim for .78 - 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight.
Some recent research shows that consuming more than 1 gram of protein per pound of body weight has negligible effects on muscle gain.
It is especially important, especially for weight loss and muscle gains, to track calories when adding more protein to your diet. An increase in calories from protein, without an other adjustments could have an adverse effect on your goals.
-
As you age, your protein needs increase. Studies show that consuming more protein can have a positive impact on maintaining ‘functionality’ and recovering quickly from illness.
Light to moderate resistance training is also extremely beneficial to maintaining strength and lean muscle mass as one ages.
RECOMMENDATION:
.45 - .6 grams per pound of bodyweight
(.99 - 1.32 grams per kg)
-
According to the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), 1 in 7 school age children (ages 6-13) do not get enough protein.
Protein is just as important, if not more important, for the mental and physical health of a growing child. Not enough protein can impact a child’s ability to concentrate, lower their immune system, delay growth and muscle development and impact their ability to recover quickly from illness or injury.
RECOMMENDATION: grams/per day
AGE 1-3: 13 grams
AGE 4-8: 19 grams
AGE 9-13: 34 grams
AGE 14-18 (girls): 46 grams
AGE 14-18 (boys): 52 grams
-
Protein is essential to the growth of new cells and tissues so it makes sense that when growing a baby, the body is going to need an increased amount of the stuff.
RECOMMENDATIONS:
Early Pregnancy (before 20 weeks): .55 grams per pound of body weight (1.22 g/kg)
Late Pregnancy (after 20 weeks): .66 grams per pound of body weight (1.45 g/kg)
Lactation: .77-.86 grams per pound of body weight (1.7 - 1.9 g/kg)
New information shows that past recommendations for protein consumption during pregnancy and while breastfeeding were insufficient for both the health of mom and baby. On average, women should aim for 100 grams of protein per day throughout the entire pregnancy.

How to calculate your protein needs based on % of calories consumed daily
Let’s Do Protein Math
COUNTING BEANS
No dumb jocks here. Before hitting the gym, hit the books and exercise those mental muscles.
Follow this 4-step process and learn how to use percent of calories consumed daily to determine your ultimate protein needs.
STEP 1:
DETERMINE YOUR TOTAL CALORIC NEEDS PER DAY
STEP 2:
DETERMINE THE % OF CALORIES FROM PROTEIN YOU SHOULD CONSUME PER DAY
The percent of your daily caloric intake that should come from protein may be based on your diet, age, lifestyle, weight or strength goals or a combination of these factors. Below are some ranges to help guide your decision.
The CDC recommends 10-35% of caloric intake be from protein.
The current Western diet averages 16% of calories from protein.
If you’re looking to lose weight and keep it off, aim for around 30% of calories to be from protein.
Building strength, go for 25-30%.
STEP 3:
CALCULATE YOUR PROTEIN CALORIES
STEP 4:
CONVERT CALORIES TO GRAMS
AN EXAMPLE
Gender: Male
Age: 30
Height: 5’ 10”
Body Weight: 180 lbs
Activity Level: moderate; exercises 3-5 days a week
Goal: mild weight loss
Caloric Needs: 2518 per day
% of Calories from Protein: 30%
Amount of Calories from Protein: 755 calories
Grams of Protein Per Day: 189 grams
Using the more general method, a suggested range of protein requirements for individuals looking to lose weight (.54 - .77 grams of protein per pound of body weight), the recommended amount of protein would be 100 - 142 grams per day. These two methods of calculating protein needs vary from 100 - 189 grams. To find what is right for you, either aim for the higher amount and if you don’t quite reach it, you’ll still be in a good place to meet your goals or go for the median of about 145 grams.
In our example, it is also important to track total caloric intake per day to ensure more calories are being burned vs consumed. Consuming a greater amount of protein while under a caloric deficit will help to lose weight while maintaining or building muscle

YOU DON’T KNOW WHAT YOU DON’T KNOW UNTIL YOU KNOW
THE 7-DAY PROTEIN CHALLENGE
So back to the main question. Are you consuming the amount of protein your body needs?
There are a lot of fancy schmancy nutrition and fitness trackers out there and you should definitely check them out, especially if you are looking to achieve specific goals.
If you’re just starting out and want to get a baseline idea of how much protein you consume per day, then our super simple 7-Day Protein Tracker will do the trick. No need to make goals or dietary adjustments just yet. For 7 days, eat like you normally do while tracking the total grams of protein in everything you consume.
With this information, you can use the protein guidelines and calculators above to determine if you are in the correct range for your given inputs and if desired, build goals from there. You might be surprised by how much a little more protein in your diet can affect how you feel.
DOWNLOAD THE TRACKER AND START YOUR 7-DAY JOURNEY
You will most likely need a resource for finding the amount of protein in certain foods, especially unprocessed foods that do not come with a nutrition label. Below are a few resources and many more can be found with a quick search on the web or app store.
Check out the Plant-Based Protein Charts at the end of this article. These highlight grams of protein per serving in some of the most popular sources of plant-based proteins.
NUTRITION TRACKER RESOURCES
Website: My Food Data
Website: Free Recipe Analyzer
App: My Plate
Tons of free resources to be found at all of these places. They are great for planning, tracking, logging and comparing foods. Both have nutrition fact search tools where you can get detailed nutritional information for virtually every food you can think of and you can adjust based on your specific portion/serving size. These tools are exactly what you need to calculate your protein and calorie consumption for the 7-Day Protein Challenge.
Use Chopped Tofu’s advanced recipe search engine for protein packed meal inspiration. Discover new and delicious plant-based recipes to kick off your 7-day journey.

Delicious & Nutritious
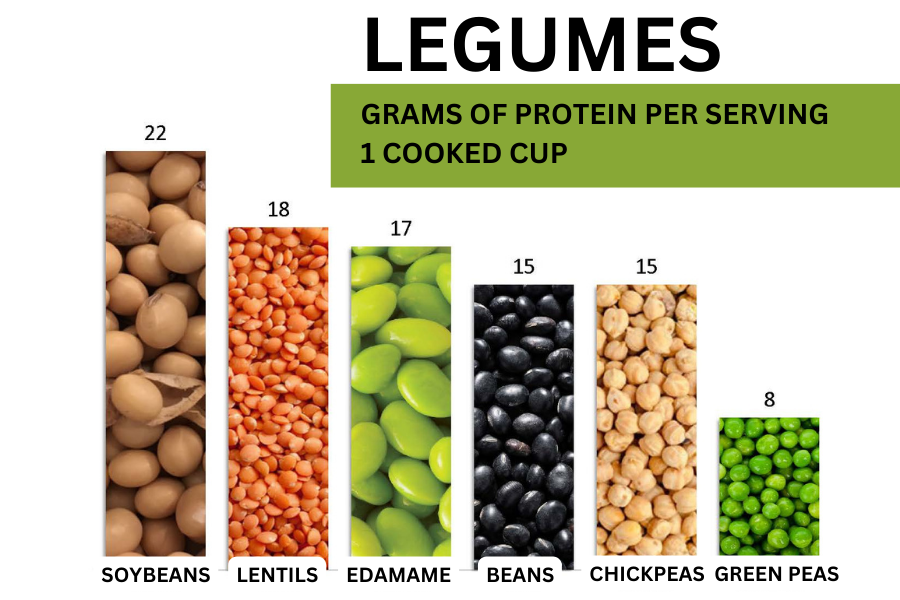
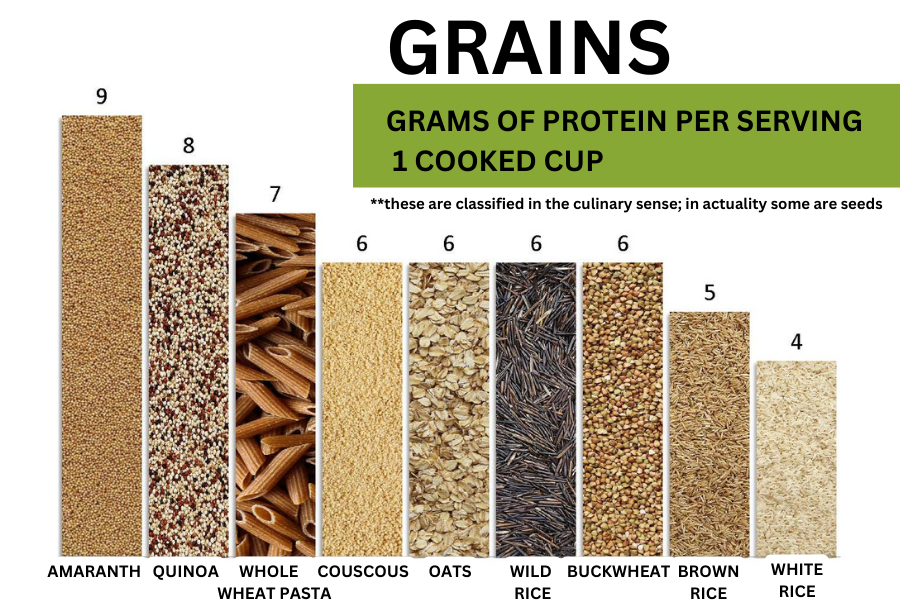
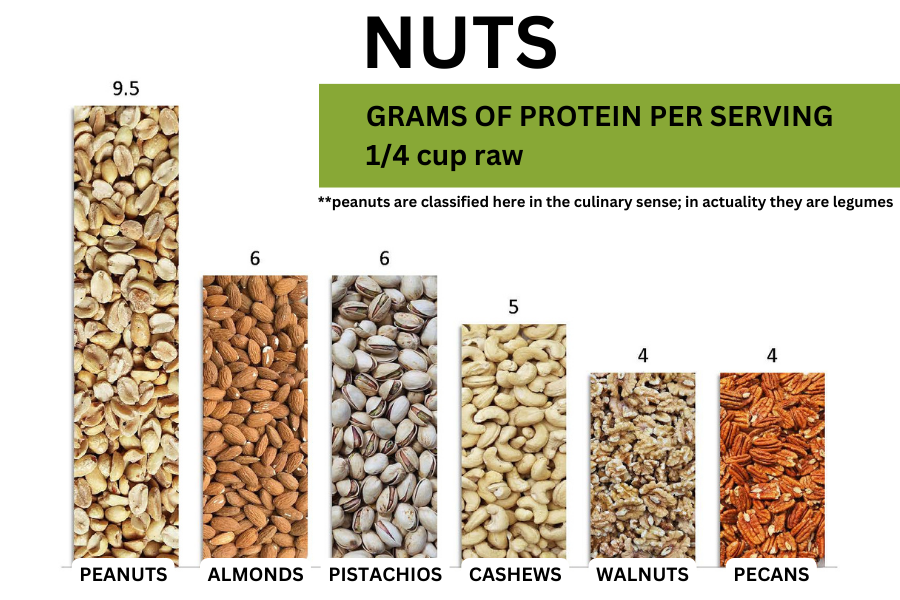
POPULAR SOURCES OF
PLANT-BASED PROTEIN
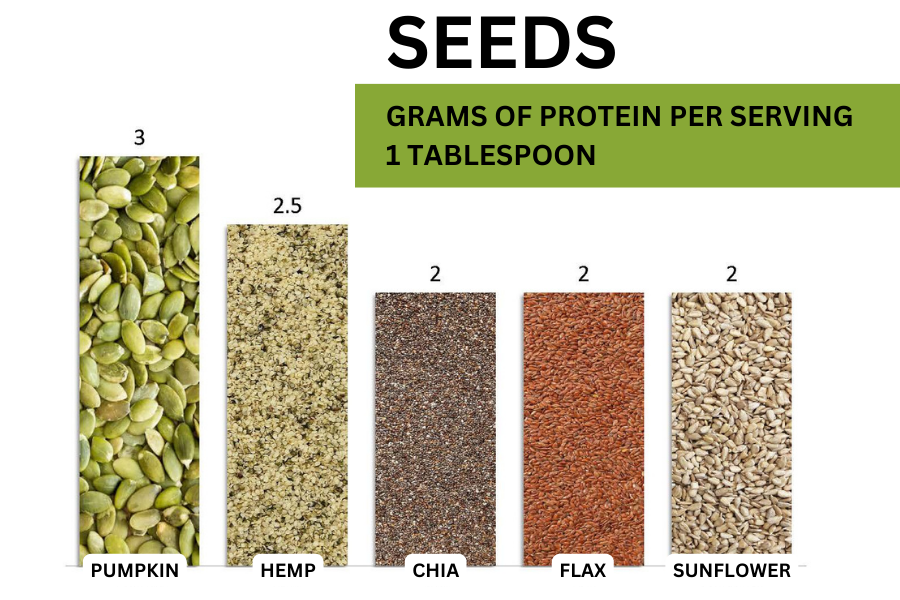
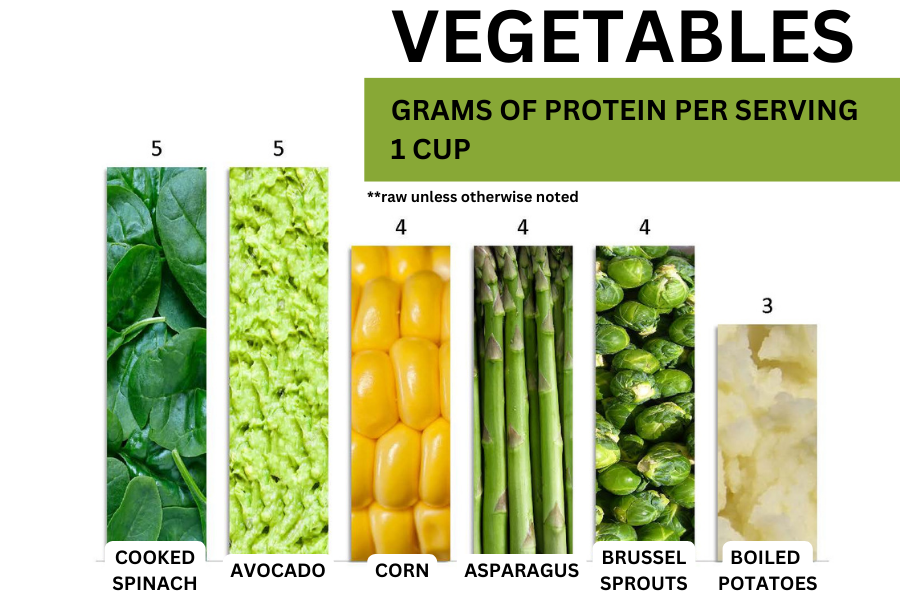
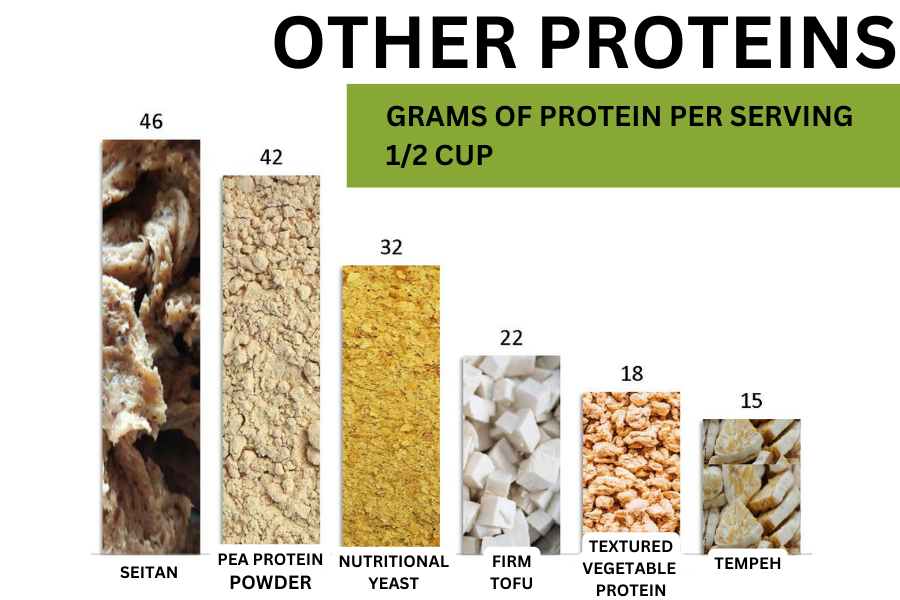
DISCLAIMER: THIS SITE IS INTENDED FOR EDUCATIONAL AND INFORMATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY AND DOES NOT PROVIDE MEDICAL ADVICE.
The information and content provided on Chopped Tofu, including linked materials, are not intended for and should not be considered medical advice. Consult a doctor for advice, diagnosis and treatment.
Chopped Tofu is not liable for risks or issues associated with advice taken from content on this site.
REFERENCES:
https://www.calculator.net/protein-calculator.html
https://www.webmd.com/diet/benefits-protein
https://www.runnersworld.com/nutrition-weight-loss/a28697827/complete-protein
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S15504131060
https://www.pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15466943
https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/how-much-protein-per-day#muscles-strength
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7997328#:~:tex
https://www.pubmed.ncib.nlm.nih.gov/22958314